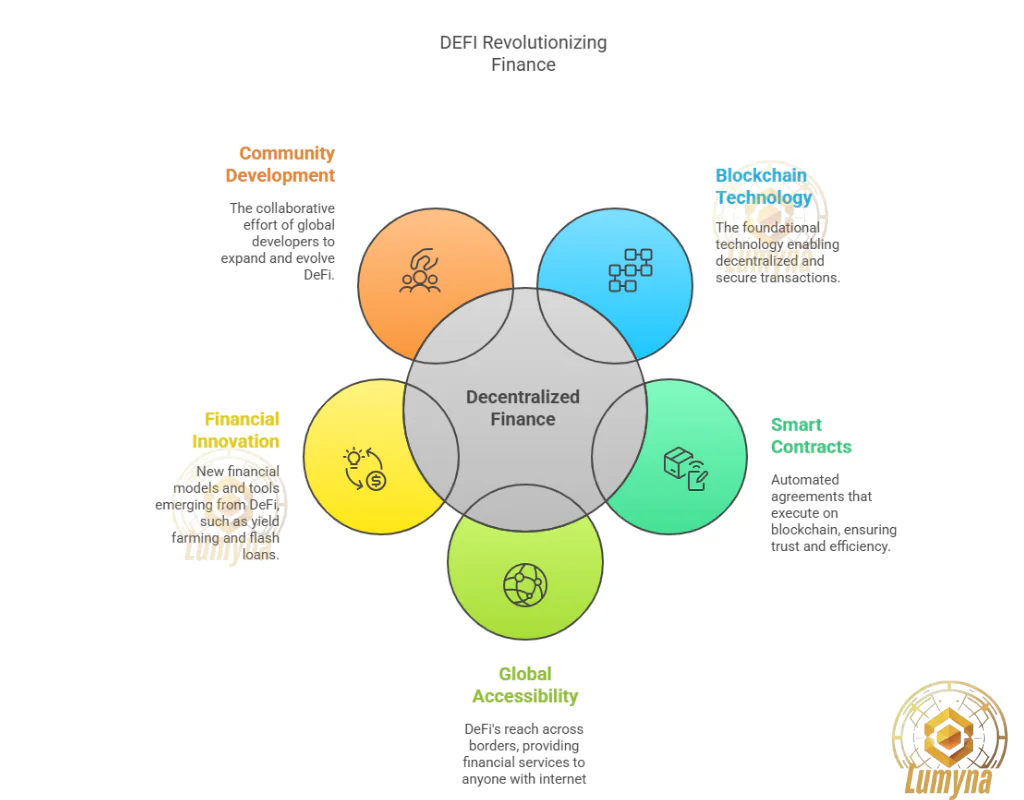
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is a blockchain-based financial system that provides services like lending, borrowing, trading, and investing without traditional intermediaries such as banks or brokers. It uses decentralized networks, primarily Ethereum, to offer open, permissionless access to financial tools, aiming to democratize finance by replacing centralized control with automated, transparent processes.
Who created DeFi?
While Satoshi Nakamoto’s Bitcoin laid the groundwork for decentralized systems in 2009, decentalized finance as a distinct concept emerged with Ethereum’s launch in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin and team. Ethereum’s smart contract functionality enabled developers to build financial applications, or dApps, sparking the DeFi movement. Since then, a global community of developers has expanded it, with key projects like MakerDAO (2017) pioneering stablecoins and lending protocols.
When did DeFi start?
Decentralized finance gained momentum around 2017 with early platforms like MakerDAO, but it exploded in popularity during the 2020 “DeFi Summer,” when yield farming and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap surged. By 2025, it’s a maturing sector, though still evolving rapidly with new protocols and use cases.
Where can you use DeFi?
It operates globally via the internet, accessible anywhere with a connection and a crypto wallet. Users engage with it through dApps for trading on DEXs, lending on platforms like Aave, or earning interest via staking, all without geographic restrictions, unlike traditional finance.
Why use DeFi?
It eliminates intermediaries, reducing fees and delays while offering borderless, censorship-resistant financial access. It appeals to those seeking transparency, privacy, or alternatives to banks, and supports innovative tools like flash loans and yield farming, unavailable in traditional systems.
How does Decentralized Finance work?
Decentralized finance relies on smart contracts, self-executing code on blockchains, that automate financial agreements. Users connect via wallets (e.g., MetaMask), deposit crypto into protocols, and interact directly with the system. Transactions are recorded on public ledgers, ensuring trust and immutability.
Related Questions:
- Is DeFi safe? It can be, with secure storage (e.g., cold wallets), but risks like smart contract bugs, hacks, and scams persist due to its nascent state.
- What’s a popular DeFi platform? Uniswap, a DEX, is widely used for token swaps, driven by liquidity pools.
- Can DeFi replace banks? Potentially, but scalability, regulation, and user adoption remain hurdles.
- How is Decentralized Finance regulated? Largely unregulated in 2025, though authorities like the U.S. SEC are increasing scrutiny, impacting its growth and legitimacy.