What is a distributed ledger?
A distributed ledger is a database that records transactions or data across a network of multiple computers, known as nodes, without relying on a central authority. Unlike traditional ledgers managed by a single entity (e.g., a bank), it’s decentralized, ensuring that all participants maintain an identical, synchronized copy. This technology underpins systems like blockchains, enabling secure, transparent, and tamper-resistant record-keeping for applications ranging from cryptocurrencies to supply chain tracking.
Who created distributed ledgers?
The concept evolved from earlier cryptographic and database innovations, but Satoshi Nakamoto popularized it with Bitcoin in 2009. Nakamoto’s blockchain, a type of distributed ledger, demonstrated how a decentralized system could function without intermediaries. Since then, developers, corporations (e.g., IBM with Hyperledger), and consortia like R3 (behind Corda) have advanced distributed ledger technology (DLT) for diverse purposes beyond cryptocurrency.
When did distributed ledgers emerge?
While theoretical groundwork existed for decades, their practical debut came with Bitcoin’s launch on January 3, 2009. The genesis block marked the first real-world use of a distributed ledger, proving its viability. Interest surged in the 2010s as blockchain gained traction, with Ethereum (2015) and enterprise-focused DLTs expanding its scope. By 2025, it’s a cornerstone of digital innovation.
Where are distributed ledgers used?
They exist on global networks of nodes—computers run by individuals, companies, or organizations—spanning continents. Public ledgers like Bitcoin’s are accessible anywhere with internet, while private ones serve specific industries, such as finance (cross-border payments), healthcare (patient records), or logistics (tracking goods). Their decentralized nature makes them borderless and versatile.
Why use a distributed ledger?
Distributed ledgers offer unparalleled benefits: transparency, as all entries are visible to participants; security, through cryptographic protection; and immutability, preventing unauthorized changes. They eliminate the need for trusted middlemen, reducing costs, delays, and single points of failure. This resilience and trust make them ideal for applications requiring accountability, like financial settlements or verifying authenticity in supply chains.
How does a distributed ledger work?
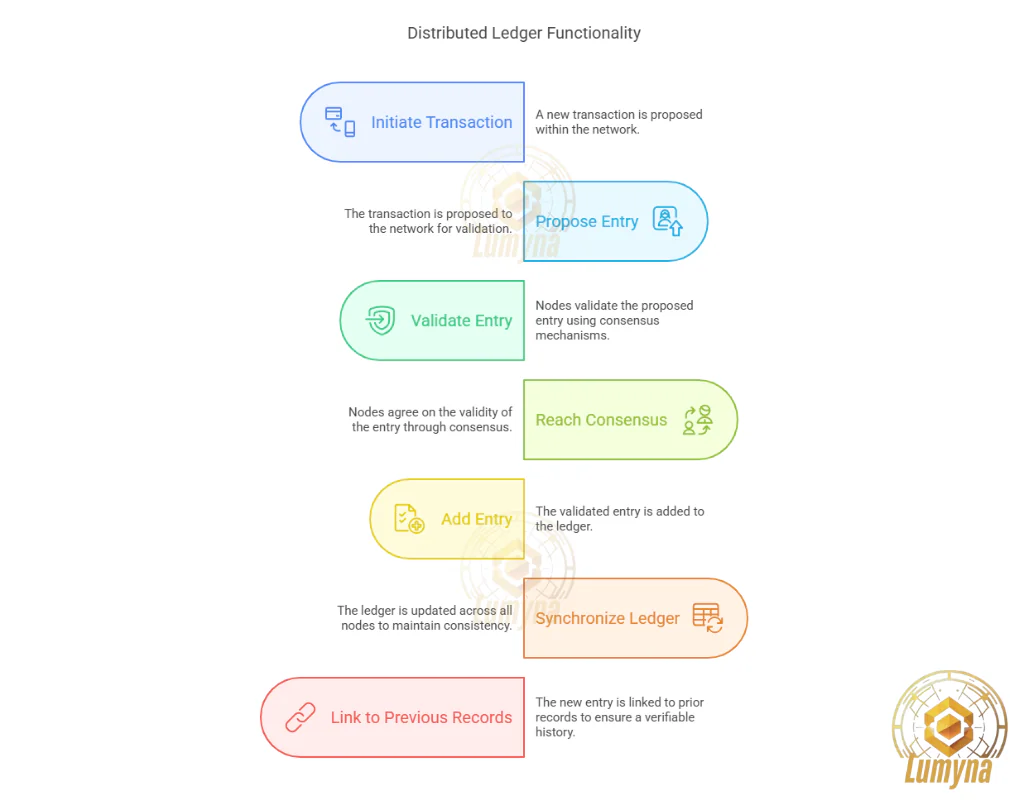
Data, such as transactions, is recorded in a shared ledger replicated across all nodes. When a new entry is proposed (e.g., a Bitcoin transfer), nodes use a consensus mechanism (like proof-of-work or proof-of-stake) to agree on its validity. Once approved, the entry is added, synchronized across the network, and linked to prior records, often in blocks, ensuring a verifiable history. This process prevents fraud and maintains consistency without centralized oversight.
Related Questions:
- Is a distributed ledger the same as a blockchain? Not exactly, blockchain is a type of distributed ledger that organizes data into chained blocks, but not all distributed ledgers (e.g., Corda) use this structure.
- What’s an example of a distributed ledger? Bitcoin’s blockchain, maintained by thousands of nodes globally, is a prime example, recording every BTC transaction since 2009.
- Can distributed ledgers be hacked? The ledger itself is highly secure due to decentralization and encryption, but vulnerabilities in user endpoints (wallets, exchanges) or flawed consensus can be exploited.
- How does it differ from a traditional database? Traditional databases are centralized, controlled by one entity, and editable by admins; distributed ledgers are shared, immutable, and rely on network consensus, prioritizing trust and redundancy.




