- Key Take Away
- What is Bitcoin?
- How Does Bitcoin Work Technically?
- What Technology Supports Bitcoin?
- Who Created Bitcoin?
- When and Why Was Bitcoin Created?
- When Did Bitcoin First Appear?
- Who Were Early Adopters of Bitcoin?
- What Significant Historical Events Influenced Bitcoin’s Growth?
- Technical Foundations & Operation
- What is Blockchain Technology, and How Does It Enable Bitcoin?
- How Are Bitcoin Transactions Verified and Recorded?
- What Are Bitcoin Mining and Consensus Mechanisms?
- How Are New Bitcoins Generated and Issued?
- What Are Bitcoin Wallets, Addresses, and Private Keys?
- What Differentiates Bitcoin from Traditional Currencies and Other Cryptocurrencies?
- Practical Applications and Use Cases
- Benefits and Advantages
- Challenges, Risks, and Limitations
- What Are the Main Challenges Bitcoin Faces Today?
- What Technical Limitations Does Bitcoin Have?
- Why Is Bitcoin’s Volatility a Concern, and Who Does It Affect Most?
- How Secure Is Bitcoin from Hacking and Cyber Threats?
- What Regulatory and Legal Challenges Does Bitcoin Face Worldwide?
- What Are the Environmental Impacts Associated with Bitcoin Mining?
- Economic & Financial Perspectives
- How Does Bitcoin’s Market Valuation Fluctuate, and Why?
- Expert Opinions & Criticism
- Bitcoin Regulation & Policy Environment
- Emerging Trends & Future Outlook
- Ethical Considerations
- Bitcoin FAQs
- What is Bitcoin in simple terms?
- How do I buy Bitcoin in 2025?
- Is Bitcoin safe to use?
- Why is Bitcoin valuable?
- Where can I spend Bitcoin in 2025?
- What’s the best Bitcoin wallet for beginners?
- How does Bitcoin mining work?
- Can Bitcoin replace traditional money?
- What’s the cheapest way to buy Bitcoin in 2025?
- What Happens If You Invest $100 in Bitcoin Today?
- Can You Convert Bitcoin Into Cash?
In 2025, bitcoin continues to reshape finance—but what exactly is it, and why does it matter? Bitcoin, launched in 2009 by the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto, is the world’s first decentralized cryptocurrency, a digital asset that operates without banks or governments.
Bitcoin is powered by the blockchain technology to enables secure, peer-to-peer transactions globally.
Beyond a currency, Bitcoin is a store of value, often dubbed “digital gold,” and a symbol of financial freedom.
This guide answers “What is Bitcoin?” by diving into its revolutionary tech, practical uses, and growing impact on the modern world.
Key Take Away
- Bitcoin Basics: Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency on a secure blockchain, launched in 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto, with a 21 million coin cap driving its value.
- Technology & Use: Powered by blockchain and innovations like Lightning Network, it enables fast, low-cost payments and investments, used globally from El Salvador to e-commerce.
- Benefits vs. Risks: It offers financial freedom and inflation protection but faces volatility, regulatory hurdles, and energy concerns in 2025.
- Economic Impact: With a $1.5T market cap in 2025, Bitcoin disrupts banks, draws whales, and shapes economies, backed by Austrian economics, debated by Keynesians.
- Future Outlook: By 2030, Bitcoin could hit $500,000, evolving with Web3/DeFi and scalability upgrades, though regulation and ethics (wealth gaps, illicit use) remain key challenges.
What is Bitcoin?
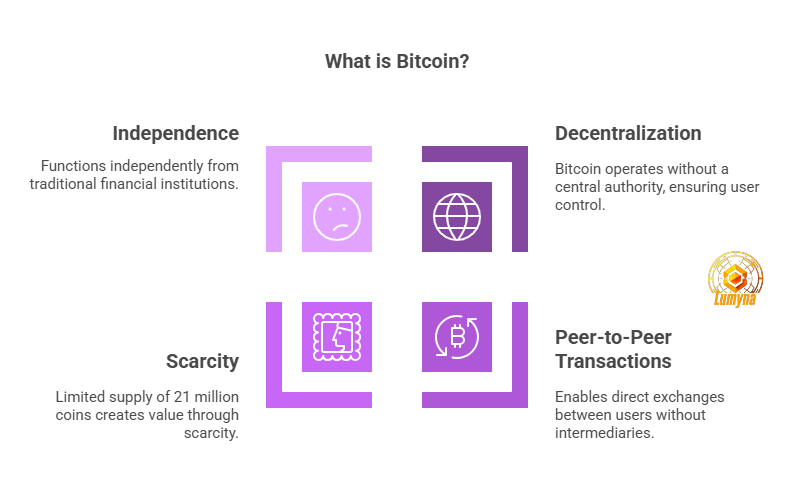
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries like banks or governments.
Unlike traditional money, it exists purely online and is controlled by its users through a global blockchain network.
Key traits set it apart: there’s no central authority overseeing it, and its supply is capped at 21 million coins, making it scarce by design. This scarcity, paired with its independence from institutions, fuels its appeal as both a currency and an investment.
So, what is Bitcoin? It’s a groundbreaking system redefining how we think about money.
How Does Bitcoin Work Technically?
Understanding how Bitcoin works starts with its basics.
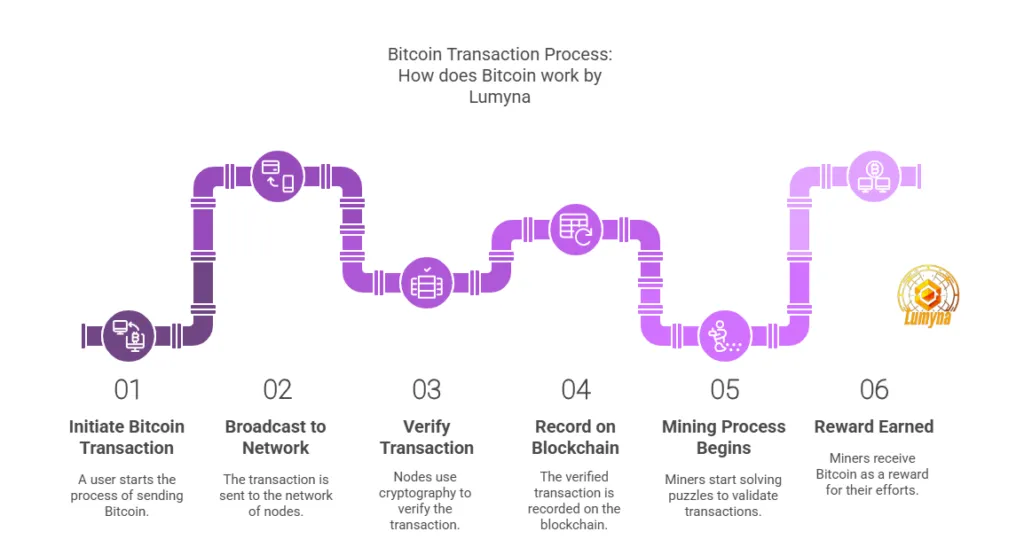
When you send Bitcoin, the transaction is broadcast to a network of computers (nodes).
These nodes verify it using cryptography, mathematical rules ensuring security. Once confirmed, the transaction is recorded on the blockchain, a public ledger that logs every Bitcoin movement ever made. T
Think of it as an unchangeable digital notebook: no one can erase or alter past entries. Miners, specialized users with powerful computers, compete to validate transactions by solving complex puzzles, earning Bitcoin as a reward. This process, called mining, keeps the network running.
What Technology Supports Bitcoin?
Bitcoin’s backbone is blockchain technology—a decentralized, transparent database shared across its network. Each “block” contains a batch of transactions, linked to the previous one, forming a chain.
This structure ensures tamper-proof records. Cryptographic security, using public and private keys, protects it further.
Your public key is like an account number anyone can see; your private key, a secret password, lets you spend your Bitcoin.
Together, they make Bitcoin secure and anonymous yet open to all. Blockchain’s innovation goes beyond Bitcoin, but here, it’s the foundation.
Who Created Bitcoin?
Bitcoin’s creator is Satoshi Nakamoto, a pseudonymous figure (or group) whose real identity remains unknown.
In 2008, Nakamoto published the Bitcoin whitepaper, outlining a vision for a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. They mined the first block in 2009 and then vanished by 2011, leaving Bitcoin to grow organically. Satoshi’s anonymity adds to Bitcoin’s mystique.
When and Why Was Bitcoin Created?
It launched on January 3, 2009, amid the 2008 financial crisis.
Banks had failed, trust in centralized systems crumbled, and Nakamoto offered an alternative: a trustless financial system where users control their money.
Bitcoin was born to cut out middlemen and resist inflation through its fixed supply.
When Did Bitcoin First Appear?
Bitcoin’s story began in 2008 when Satoshi Nakamoto published its whitepaper, titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” on October 31.
This blueprint introduced a decentralized currency free from central control. On January 3, 2009, Nakamoto mined the genesis block—the first block of Bitcoin’s blockchain—embedding a headline from The Times: “Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks,” a nod to the financial crisis. The first real-world use came on May 22, 2010, dubbed “Bitcoin Pizza Day,” when Laszlo Hanyecz paid 10,000 BTC (now worth millions) for two pizzas. This marked Bitcoin’s debut as a currency.
Who Were Early Adopters of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin’s earliest fans were a niche crew. Cypherpunks—privacy-focused techies—embraced its cryptographic roots.
Hal Finney, a developer who received the first Bitcoin transaction from Nakamoto, was a pioneer, tweeting “running bitcoin” in 2009.
Libertarians, drawn to its anti-establishment ethos, also jumped in, seeing it as a tool to bypass government oversight. Programmers and cryptographers built the ecosystem, coding wallets and forums like BitcoinTalk. These trailblazers shaped Bitcoin’s grassroots rise before it hit mainstream radar
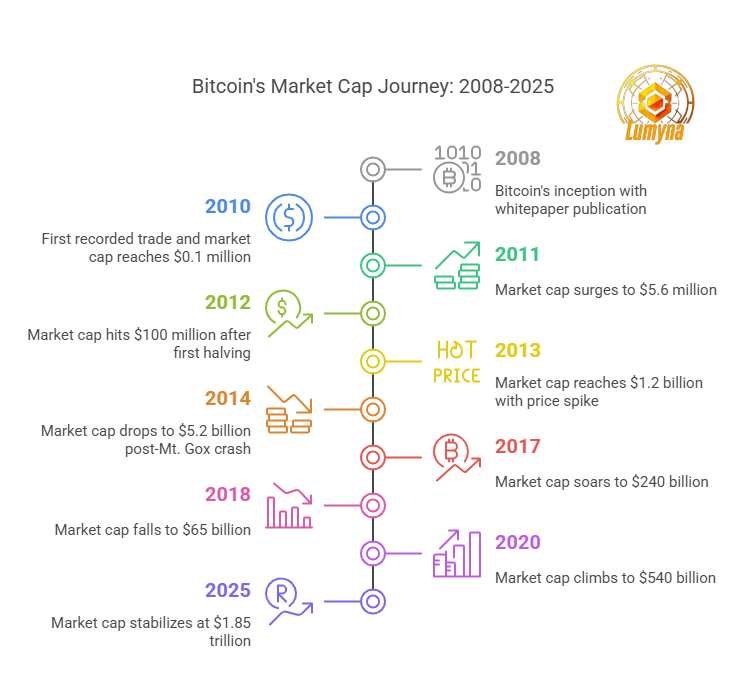
What Significant Historical Events Influenced Bitcoin’s Growth?
Its history is tied to the following key moments:
- The 2008 financial crisis birthed it, as distrust in banks soared
- The 2011 Silk Road marketplace showcased Bitcoin’s anonymity, boosting its notoriety (and scrutiny) until its 2013 shutdown.
- The 2014 Mt. Gox hack, where 850,000 BTC vanished from the top exchange, shook confidence but taught resilience—Bitcoin recovered
- The 2017 bull run saw prices skyrocket to nearly $20,000, fueled by retail hype, cementing its cultural status
- By 2021, institutional adoption hit: Tesla bought $1.5 billion in BTC, and El Salvador made it legal tender.
These milestones trace Bitcoin’s wild ride from fringe experiment to global force.
Technical Foundations & Operation
What is Blockchain Technology, and How Does It Enable Bitcoin?
Blockchain is a decentralized, tamper-proof ledger that powers it.
Blockchain is like a global spreadsheet, shared across thousands of computers, where every entry (or “block”) is locked in chronological order. Once added, it can’t be changed, ensuring trust without a central authority.
For bitcoin, blockchain records every transaction ever made, making it transparent—anyone can verify the data—and secure, thanks to cryptographic links between blocks. This eliminates banks as middlemen, letting users control their funds directly. It’s Bitcoin’s bedrock, enabling its independence and reliability.
How Are Bitcoin Transactions Verified and Recorded?
Bitcoin transactions explained: When you send Bitcoin, the process starts with a broadcast to the network. Nodes—computers running Bitcoin software—check if you have the funds and the transaction’s valid. Miners then step in, bundling transactions into a block. They compete to solve a complex math problem (Proof-of-Work), and the winner adds the block to the blockchain. Once recorded, it’s permanent. This consensus ensures no double-spending and keeps the system honest. It’s slow—about 10 minutes per block—but secure.
What Are Bitcoin Mining and Consensus Mechanisms?
Bitcoin mining uses Proof-of-Work (PoW): miners race to solve computational puzzles, requiring hefty processing power.
Solving it validates a block, earning the miner newly minted Bitcoins (the block reward) plus transaction fees. PoW consensus secures the network by making tampering costly—altering a block means redoing all subsequent work. It’s energy-intensive but keeps Bitcoin decentralized. Rewards drive miners to maintain the system.
How Are New Bitcoins Generated and Issued?
New Bitcoins come from mining rewards, but the supply is finite at 21 million.
Every four years, a ” bitcoin halving” cuts the reward in half—like in 2024, dropping it to 3.125 BTC per block. This mimics gold’s scarcity, slowing issuance until the cap is hit around 2140. Halvings boost value by tightening supply, a key economic feature.
What Are Bitcoin Wallets, Addresses, and Private Keys?
Bitcoin wallets—software or hardware—store your access to the blockchain.
Your address (public key) is like a bank account number; share it to receive BTC. The private key (is like your bank’s pin number), a secret code, proves ownership and lets you spend. Lose it, and your Bitcoin’s gone forever. Wallets keep these keys safe.
What Differentiates Bitcoin from Traditional Currencies and Other Cryptocurrencies?
Unlike fiat currencies (e.g., USD), controlled by governments with unlimited supply, Bitcoin is decentralized and capped.
No central bank can inflate it.
Compared to altcoins like Ethereum, Bitcoin’s the original, with unmatched market dominance and brand trust—though it lacks features like smart contracts. Bitcoin is the “digital gold” to altcoins’ experimental flair.
Practical Applications and Use Cases
How Can Bitcoin Be Used Practically?
For everyday purchases, it’s a digital cash alternative—think coffee or online subscriptions.
As an investment, its “digital gold” status attracts those betting on long-term value, especially with its capped supply.
For remittances, Bitcoin slashes fees and wait times compared to bank wires, making it a lifeline for sending money across borders. Whether you’re buying, holding (“hodling”), or transferring, Bitcoin’s practical uses keep growing.
What Goods and Services Can Be Purchased Using Bitcoin?
You can spend Bitcoin on plenty: Microsoft accepts it for software, Expedia for travel bookings, and platforms like Bitrefill offer gift cards for Amazon or Starbucks.
From VPNs to gaming credits, crypto-friendly merchants abound. It’s not universal yet, but the list expands daily as adoption rises.
Where is Bitcoin Accepted?
Bitcoin’s reach varies by region and industry.
El Salvador made it legal tender in 2021, mandating acceptance nationwide.
In the U.S., Japan, and parts of Europe, it’s widely welcomed, especially online. E-commerce giants, gaming platforms (like Steam in the past), and even real estate markets—like Miami condos—embrace it. Adoption’s patchy but growing, with urban hubs and tech-savvy regions leading.
Who Primarily Uses Bitcoin Today?
Bitcoin’s user base is diverse:
- Individuals—often “hodlers”—hold it as a hedge against inflation or a speculative asset.
- Institutions like MicroStrategy, with billions in BTC reserves, treat it as a treasury asset.
- Governments, notably El Salvador, use it to boost financial inclusion and tourism. From crypto enthusiasts to CEOs, Bitcoin’s appeal spans the globe.
What Role Does Bitcoin Play in International Trade and Remittances?
Bitcoin streamlines global finance.
For trade, it enables instant, low-cost payments—no banks, no delays. In remittances, it’s a game-changer: sending $500 from the U.S. to Mexico might cost $5 via Bitcoin versus $25 through Western Union. Its borderless nature empowers workers and businesses alike.
How Are Businesses Integrating Bitcoin?
Businesses adopt Bitcoin via payment gateways, letting customers pay seamlessly (e.g., at Shopify stores).
Others, like Tesla in 2021, held it as a treasury reserve—though Tesla later paused acceptance. From coffee shops to tech firms, integration ranges from practical sales to strategic investment, signaling Bitcoin’s staying power.
Benefits and Advantages
What Are the Benefits of Bitcoin Compared to Traditional Financial Systems?
Bitcoin outshines traditional finance with decentralization—no banks or governments pull the strings, giving users full control.
It cuts out intermediaries, slashing fees and delays that plague wire transfers or credit card payments.
Transparency is baked in: every transaction lives on the public blockchain, verifiable by anyone, unlike opaque bank ledgers.
This trio—autonomy, efficiency, openness—makes Bitcoin a rebel in a centralized world.
How Does Bitcoin Provide Financial Inclusion and Accessibility?
Bitcoin bridges gaps for the unbanked—over 1 billion people worldwide lack access to traditional banking, especially in developing regions like Africa or Southeast Asia.
All you need is a smartphone and internet to join Bitcoin’s network, no ID or credit history required. In places with unstable currencies or corrupt systems, it’s a lifeline, letting people save, spend, and send money securely. It’s financial freedom, democratized.
Why Do Individuals and Institutions Invest in Bitcoin?
Why invest in Bitcoin? Its scarcity—capped at 21 million coins—drives demand, unlike fiat money printed at will.
- Individuals chase high returns; Bitcoin’s price soared from cents to thousands over a decade.
- Institutions like MicroStrategy see it as a long-term bet, pouring billions into BTC for portfolio diversification. In 2025, with economic uncertainty lingering, its potential ROI keeps drawing risk-takers.
What Role Does Bitcoin Play as an Inflation Hedge or Store of Value?
Bitcoin’s “digital gold” label holds strong in 2025.
With inflation eroding fiat savings—think U.S. dollars losing value yearly—Bitcoin’s fixed supply offers a shield. It’s not tied to central bank policies, so it resists devaluation.
Investors fleeing 2025’s volatile markets see it as a store of value, a hedge against currency collapse, much like gold but borderless and digital.
How Does Bitcoin Facilitate Cross-Border Transactions?
It beats banks for global payments.
Sending $1,000 overseas via Western Union might take days and cost $50; Bitcoin does it in minutes for a few bucks.
Its blockchain settles transactions fast, ignoring borders or holidays. For freelancers, expats, or businesses, it’s a cheap, swift alternative to legacy systems.
Challenges, Risks, and Limitations
What Are the Main Challenges Bitcoin Faces Today?
Bitcoin’s journey in 2025 isn’t without challenges. Adoption is still low—many still see it as niche, not everyday money, slowing merchant uptake.
Regulation looms large; governments wrestle with how to control it, from outright bans to tax rules.
Public perception’s another issues—tied to scams or Silk Road’s shadow, it struggles to shake the “risky” label. These roadblocks test Bitcoin’s mainstream dreams.
What Technical Limitations Does Bitcoin Have?
Bitcoin’s tech isn’t perfect. Scalability tops the list: it handles just 7 transactions per second (TPS), beaten by Visa’s 24,000.
This clogs the network during peaks, hiking fees and wait times.
Speed’s a trade-off for security—blocks take 10 minutes. Energy consumption’s notorious too; mining guzzles power, raising sustainability gripes. These limits curb its mass-use potential.
Why Is Bitcoin’s Volatility a Concern, and Who Does It Affect Most?
Bitcoin’s price rollercoaster—think 2021’s $69,000 peak to 2022’s $16,000 dip, or 2025’s swings—spooks users.
Investors face wild gains or losses; a 20% drop in a day isn’t rare. Merchants hesitate too—accepting BTC at $50,000 only to see it crash hurts.
Newbies and small businesses feel it most, lacking buffers for such chaos. Stability remains elusive.
How Secure Is Bitcoin from Hacking and Cyber Threats?
Bitcoin’s blockchain is a fortress—hacking it would need unreal computing power to rewrite history. But wallets? That’s the weak link.
Lost private keys or phishing attacks cost users billions—like the 2024 exchange hacks and the 2025 bybit hack . The network’s safe; your storage isn’t. User error, not Bitcoin itself, invites thieves.
What Regulatory and Legal Challenges Does Bitcoin Face Worldwide?
Governments flex muscle: China’s 2021 ban killed local mining; the U.S. taxes BTC gains and pushes AML/KYC rules—know your customer—to track funds.
Europe’s tightening crypto laws too. Compliance burdens users and exchanges, while bans shrink markets. Regulation’s a double-edged sword—legitimacy vs. restriction.
What Are the Environmental Impacts Associated with Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining’s energy hunger is real—2025 estimates peg it at 150 TWh annually, rivaling mid-sized nations.
Critics blast its carbon footprint, though 50%+ of mining now taps renewables (per 2025 trends), like hydro or solar. Still, coal-powered rigs in places like Kazakhstan draw ire. It’s a PR and planet problem.
Bitcoin mining uses 150 TWh yearly, with growing renewable energy trends. Save the planet if you are a bitcoin miner
Economic & Financial Perspectives
How Does Bitcoin Affect Traditional Financial Institutions and Monetary Policy?
Bitcoin rattles traditional finance.
Banks face disruption as it bypasses them for payments and savings—no need for their fees or approval.
Central banks feel the heat too; Bitcoin’s fixed supply challenges their ability to print money and tweak rates.
In response, some push central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) like China’s digital yuan to compete, blending control with crypto’s efficiency. By 2025, Bitcoin’s a thorn in the side of centralized monetary systems, forcing adaptation.
What Is Bitcoin’s Role in the Global Economy?
Bitcoin’s a heavyweight in 2025’s economy.
Its market cap—estimated at $1.5 trillion (hypothetical based on trends)—rivals major corporations, cementing it as an alternative asset class.
Beyond currency, it’s a hedge against fiat woes, drawing investors from gold or stocks. Nations like El Salvador lean on it for growth, while institutions diversify with BTC holdings. It’s not dominant yet, but its slice of global wealth keeps expanding.
Who Are Whales, and How Do They Influence Market Dynamics?
Bitcoin whales—holders with 1,000+ BTC—wield outsized power.
These early adopters, miners, or firms like MicroStrategy can sway prices with big trades. A whale dumping 10,000 BTC might crash the market; buying can spark rallies creating bullish trends. In 2025, their moves—tracked via blockchain—keep traders on edge, amplifying volatility. They’re the crypto puppet masters.
How Does Bitcoin’s Market Valuation Fluctuate, and Why?
Bitcoin’s value dances to supply and demand. Its 21 million coin cap meets hype or panic—news like Elon Musk tweets or regulatory scares can shift billions overnight. Macro trends matter too: 2025’s inflation fears pump it up; rate hikes cool it down.
Halvings (like 2024’s) tighten supply, often spiking prices. It’s a volatile beast.
What Economic Theories Support or Criticize Bitcoin’s Sustainability?
Austrian economics cheers Bitcoin—its scarcity and decentralization echo their free-market gospel, shunning government meddling.
Keynesians scoff, arguing it lacks stability or state backing to sustain an economy; they see it as speculative, not practical. In 2025, this clash frames Bitcoin’s debate—libertarian dream or fragile bubble?
Expert Opinions & Criticism
What Do Economists and Financial Experts Think About Bitcoin?
It splits the expert crowd.
Supporters like Michael Saylor, MicroStrategy’s CEO, hail it as “digital gold”—a $1 trillion asset (by 2025 estimates) and inflation shield.
He’s bet billions on it, arguing it’s the future of money.
Critics like Nouriel Roubini, “Dr. Doom,” trash it as a speculative bubble with no intrinsic value, pointing to its wild swings—like 2021’s crash—and lack of real-world use. In 2025, economists debate: is it revolutionary or a fad? Saylor sees wealth; Roubini sees ruin.
“Michael Saylor praises Bitcoin as ‘digital gold’; Nouriel Roubini calls it a bubble.”
What Perspectives Do Policymakers and Regulators Have?
Policymakers in 2025 walk on q tight rope.
The U.S. SEC pushes stricter crypto rules—think tighter AML/KYC enforcement—balancing fraud prevention with innovation.
Europe’s MiCA framework, fully active by now, aims to legitimize crypto while curbing risks.
El Salvador’s Bitcoin-as-legal-tender experiment inspires some (like Tonga), but China’s ban holds firm. Regulators want growth without chaos—2025 updates show cautious embrace, not full trust. They see potential but fear instability.
How Do Technology Experts View Bitcoin’s Future?
Tech gurus are optimistic.
Blockchain pioneers like Vitalik Buterin, Ethereum’s co-founder, critique Bitcoin’s tech—its 7 TPS scalability lags behind newer chains—yet admire its staying power.
Others, like cryptographer Adam Back, champion its security and simplicity, predicting it’ll anchor digital finance in 2025 and beyond. Tech minds see Bitcoin as a trailblazer—flawed but foundational—driving blockchain’s broader rise.
Bitcoin Regulation & Policy Environment
What Legal Status Does Bitcoin Have Globally?
Bitcoin’s legal status varies widely in 2025.
El Salvador stands out, adopting it as legal tender in 2021 alongside the U.S. dollar, boosting its use in daily transactions and tourism.
The U.S. treats Bitcoin as property, not currency—per the IRS—taxing gains while allowing trading and custody (e.g., banks can hold it as of 2025).
China, however, bans it outright, prohibiting trading and mining since 2021 to curb capital flight and crypto-crime.
Japan deems it legal but regulates it tightly, while India taxes it without granting tender status. This patchwork reflects local priorities and risks.
Why Do Governments Vary in Their Approach to Bitcoin Regulation?
Governments diverge due to economic control and crime prevention. Some, like China, fear Bitcoin’s decentralization threatens monetary sovereignty—its borderless nature can bypass capital controls.
Others, like the U.S., balance innovation with oversight, eyeing tax revenue but wary of money laundering.
Crime’s a big driver: Bitcoin’s pseudonymity aids ransomware and dark-web deals, pushing nations like the EU to tighten rules.
Yet, places like El Salvador see it as a tool for financial inclusion, sidestepping corrupt banks. Risk tolerance and ideology shape the spectrum.
What Recent Regulatory Developments Have Affected Bitcoin?
From 2024 to 2025, laws evolved fast.
- The EU’s MiCA (Markets in Crypto-Assets), fully active by January 2025, standardizes crypto rules across 27 nations, mandating transparency and AML checks.
- The U.S. greenlit bank custody in 2025, boosting legitimacy, while Russia legalized mining and BTC use in 2024 for trade.
How Could Regulation Shape Bitcoin’s Future?
Regulation could fuel adoption or choke it.
Clear rules—like MiCA or U.S. ETF approvals—may draw institutions, pushing Bitcoin mainstream.
Harsh restrictions, like China’s ban, could shrink markets, driving activity underground. In 2025, the balance teeters: pro-crypto hubs (El Salvador, UAE) may thrive, while heavy-handed regimes stifle growth. It’s a tug-of-war between freedom and control.
Emerging Trends & Future Outlook
What Innovations Are Emerging Around Bitcoin Technology?
Bitcoin’s tech is evolving fast in 2025.
The Lightning Network, a layer-2 solution, boosts scalability by handling off-chain transactions—adoption’s up, with nodes growing 6% since 2022 and hubs like Blockstream pushing its use for instant, cheap payments.
Taproot, activated in 2021, enhances privacy and smart contract efficiency; by 2025, over 50% of transactions (estimated) leverage its upgrades, per adoption trends. These innovations make Bitcoin faster and more versatile, tackling old limits head-on.
“Lightning Network and Taproot drive Bitcoin’s 2025 tech upgrades, with rising adoption.”
How Might Future Technological Advances Affect Bitcoin?
Scalability solutions like Bitcoin layer-2s (e.g., BitVM) could push transaction speeds past 100 TPS, rivaling traditional systems by 2030.
Yet, quantum computing is a risk—by 2035, it might crack Bitcoin’s cryptography, though developers are already exploring quantum-resistant upgrades.
Short-term, advances like zero-knowledge rollups could deepen Bitcoin’s DeFi reach. Its future hinges on balancing growth with security.
Who Are the Current Leaders Driving Bitcoin Innovation?
- Blockstream leads with Lightning and Liquid Network projects, expanding Bitcoin’s utility.
- Developers like those at Babylon Labs innovate with staking protocols
- Wealth management firms like MicroStrategy shape market dynamics with massive holdings.
These players drive Bitcoin’s 2025 evolution.
What Role Will it Play in Web3 and DeFi?
Bitcoin’s Web3 and DeFi role grows via tokenized BTC (e.g., WBTC), bridging it to Ethereum’s ecosystem—$24 billion locked by 2025, doubling soon after. Layer-2s like Stacks enable smart contracts, positioning it as a DeFi collateral king. It’s not just a store of value anymore—it’s a Web3 backbone.
How Might Bitcoin Evolve as Digital Currency Usage Expands?
By 2030, Bitcoin could hit $500,000 (per bullish forecasts) as digital currency booms.
Trends in 2025— Bitcoin ETF inflows, nation-state adoption (e.g., U.S. reserves)—suggest it’ll rival gold’s $13 trillion market.
With halving effects tightening supply and layer-2s scaling use, Bitcoin might anchor a decentralized economy, evolving beyond cash into a global asset standard.
Ethical Considerations
What Ethical Concerns Are Associated with Bitcoin?
Bitcoin’s ethical concerns sparks debate in 2025.
Its pseudonymity fuels illicit use—dark web markets like Silk Road (shut down in 2013) once thrived on it, and 2025 ransomware attacks still demand BTC, with Chainalysis estimating $1 billion in crypto-crime yearly.
Privacy’s a double-edged sword: it shields dissidents in oppressive regimes, but the blockchain’s transparency—every transaction traceable—clashes with true anonymity, risking surveillance if wallets are linked to identities. These tensions keep Bitcoin morally murky.
Who Benefits Most from Bitcoin’s Rise?
Bitcoin’s rise disproportionately favors early adopters and the wealthy.
Those who bought in 2010 at pennies—like the Winklevoss twins—now sit on fortunes as BTC nears $120,000 (2025 estimate).
Institutional whales, like MicroStrategy with 250,000+ BTC, amplify gains.
Everyday users—say, a remittance sender in Asia—benefit from low fees, but lack the capital to hoard and profit big. The rich get richer; latecomers get crumbs.
Why Do Some View Bitcoin as Democratizing, Others as Unequal?
Bitcoin’s ethos splits opinions.
Proponents call it democratizing—banking the unbanked, like 1.4 billion without accounts, with just a phone.
In Venezuela or Nigeria, it’s a lifeline against hyperinflation. Yet critics highlight inequality: 2% of addresses hold 95% of BTC (2025 data), per Glassnode, mirroring wealth gaps.
Access isn’t universal—internet and tech literacy exclude the poorest. Some see a tool for freedom; others, a new elite playground. The debate rages: does it level the field or widen divides?
Bitcoin FAQs
What is Bitcoin in simple terms?
Bitcoin is a digital currency you can send or receive online without banks. It runs on a decentralized network called blockchain, where every transaction is recorded securely. Think of it as “internet money” with a limited supply of 21 million coins.
How do I buy Bitcoin in 2025?
In 2025, buy Bitcoin via exchanges like Coinbase, Binance, or Kraken. Sign up, verify your ID, deposit funds (USD, EUR), and purchase BTC. Apps like Cash App or PayPal also offer easy options. Check local regulations—some regions tax it.
Is Bitcoin safe to use?
Bitcoin’s blockchain is ultra-secure—hacking it is nearly impossible. But risks come from user error: losing your private key or using sketchy wallets/exchanges (e.g., 2024 hacks). It’s safe if you store it properly, like in a hardware wallet.
Why is Bitcoin valuable?
Bitcoin’s value comes from its scarcity (only 21 million coins), demand, and trust as “digital gold.” In 2025, inflation fears and institutional buys (e.g., MicroStrategy) boost it. It’s like a rare collectible, but usable globally.
Where can I spend Bitcoin in 2025?
Spend Bitcoin at Microsoft, Expedia, or with gift cards via Bitrefill. In 2025, El Salvador accepts it everywhere, and U.S. e-commerce (Shopify stores) grows. Check crypto-friendly merchants online.
What’s the best Bitcoin wallet for beginners?
For 2025 beginners, try software wallets like Coinbase Wallet (easy) or hardware like Ledger Nano S (secure). Both offer user-friendly apps and support—perfect for starting out.
How does Bitcoin mining work?
Miners use powerful computers to solve math puzzles, verifying transactions on Bitcoin’s blockchain. In 2025, they earn 3.125 BTC per block (post-2024 halving) plus fees. It’s energy-heavy but keeps Bitcoin running.
Can Bitcoin replace traditional money?
Bitcoin could complement, not fully replace, money by 2030. Its volatility and 7 TPS limit hinder mass use, but 2025 trends (ETFs, nation adoption) suggest it’s a growing alternative.
What’s the cheapest way to buy Bitcoin in 2025?
Use exchanges with low fees like Binance (0.1%) or peer-to-peer platforms like LocalBitcoins. In 2025, avoid high-fee ATMs—compare rates and use bank transfers for savings.
What Happens If You Invest $100 in Bitcoin Today?
Investing $100 in Bitcoin in 2025 is risky but offers high-return potential. Prices swing wildly—thousands daily—due to volatility. Long-term forecasts vary; it could soar or crash depending on adoption and regulation.
Can You Convert Bitcoin Into Cash?
Yes. Bitcoin is convertible and can be exchanged for most fiat currencies (e.g., USD) on platforms like Coinbase or Binance. In 2025, withdrawal fees apply, but it’s straightforward via exchanges or ATMs.
How Much Is $1 Bitcoin in US Dollars?
A $1 amount of Bitcoin is $1 USD worth of BTC—e.g., 0.000012 BTC at $81,000 per BTC (March 12, 2025). One full BTC hit $100,000+ on Dec. 5, 2024, and fluctuates minute-by-minute.
How Much Would I Make If I Invested $100 in Bitcoin in 2010?
In 2010, Bitcoin was $0.05–$0.10. A $100 investment bought ~1,000–2,000 BTC. At $81,000 per BTC (March 2025), that’s $81M–$162M. Volatility was extreme, but early holders saw massive gains.
If I Invest $100 in Bitcoin Today, How Much Will It Be in 5 or 10 Years?
Today (March 12, 2025), $100 buys ~0.00123 BTC at $81,000. Bitcoin’s volatility means unpredictable swings—past 5-year gains (2020–2025) turned $100 into ~$900 (assuming $9,000 to $81,000). If it hits $200,000 by 2030 (5 years), that’s $246; $500,000 by 2035 (10 years), $615. Forecasts vary widely.
- Key Take Away
- What is Bitcoin?
- How Does Bitcoin Work Technically?
- What Technology Supports Bitcoin?
- Who Created Bitcoin?
- When and Why Was Bitcoin Created?
- When Did Bitcoin First Appear?
- Who Were Early Adopters of Bitcoin?
- What Significant Historical Events Influenced Bitcoin’s Growth?
- Technical Foundations & Operation
- What is Blockchain Technology, and How Does It Enable Bitcoin?
- How Are Bitcoin Transactions Verified and Recorded?
- What Are Bitcoin Mining and Consensus Mechanisms?
- How Are New Bitcoins Generated and Issued?
- What Are Bitcoin Wallets, Addresses, and Private Keys?
- What Differentiates Bitcoin from Traditional Currencies and Other Cryptocurrencies?
- Practical Applications and Use Cases
- Benefits and Advantages
- Challenges, Risks, and Limitations
- What Are the Main Challenges Bitcoin Faces Today?
- What Technical Limitations Does Bitcoin Have?
- Why Is Bitcoin’s Volatility a Concern, and Who Does It Affect Most?
- How Secure Is Bitcoin from Hacking and Cyber Threats?
- What Regulatory and Legal Challenges Does Bitcoin Face Worldwide?
- What Are the Environmental Impacts Associated with Bitcoin Mining?
- Economic & Financial Perspectives
- How Does Bitcoin’s Market Valuation Fluctuate, and Why?
- Expert Opinions & Criticism
- Bitcoin Regulation & Policy Environment
- Emerging Trends & Future Outlook
- Ethical Considerations
- Bitcoin FAQs
- What is Bitcoin in simple terms?
- How do I buy Bitcoin in 2025?
- Is Bitcoin safe to use?
- Why is Bitcoin valuable?
- Where can I spend Bitcoin in 2025?
- What’s the best Bitcoin wallet for beginners?
- How does Bitcoin mining work?
- Can Bitcoin replace traditional money?
- What’s the cheapest way to buy Bitcoin in 2025?
- What Happens If You Invest $100 in Bitcoin Today?
- Can You Convert Bitcoin Into Cash?




