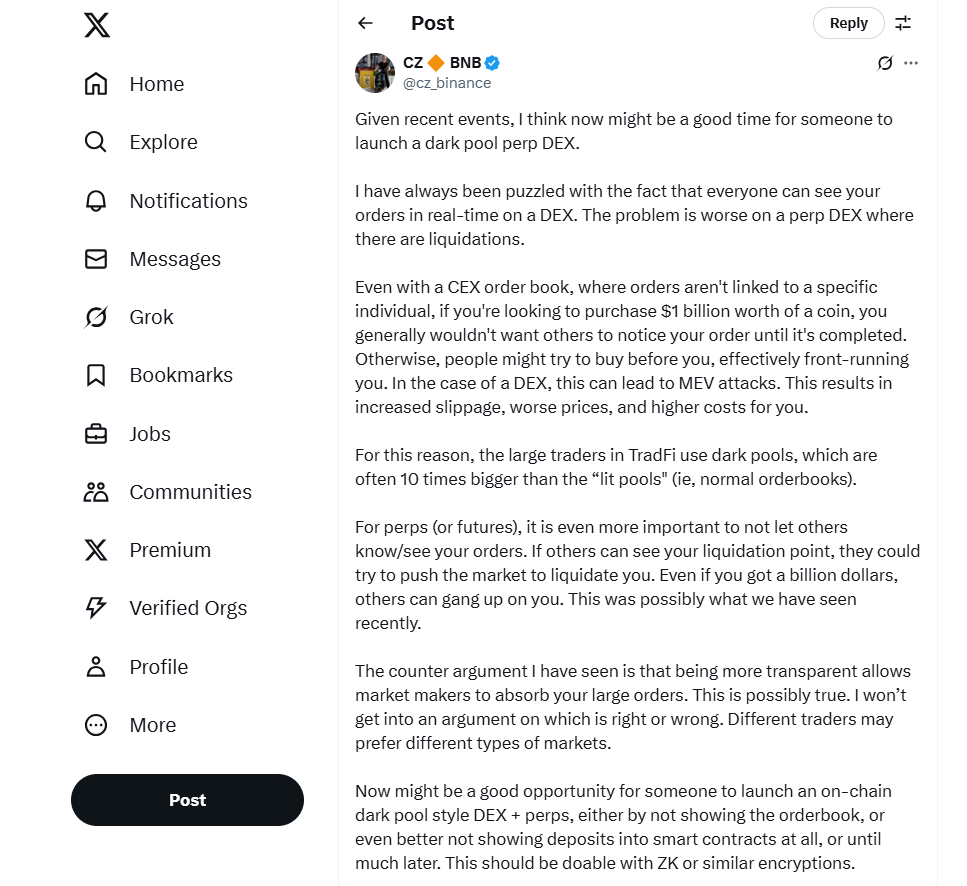
On June 1, 2025, Binance founder CZ sparked a firestorm of discussion with a single tweet, proposing a “dark pool-type perpetual contract DEX” to address the privacy pitfalls of transparent decentralized exchanges (DEXs). View CZ’s tweet here
His vision has reignited interest in dark pools, a concept borrowed from traditional finance but meant to revolutionize Web3 trading. But what exactly are dark pools, and why do they matter for the future of decentralized finance (DeFi) and perpetual contracts?
Lumyna Insights dives deep into the mechanics, benefits, challenges, and pioneering projects driving this privacy-centric innovation.
What Are Dark Pools?
Origins in Traditional Finance
Dark pools aren’t a Web3 invention—they’ve been a fixture in traditional finance since the late 1970s. In 1979, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) introduced Regulation 19c-3, allowing securities to trade off public exchanges. The 1980s rise of high-frequency trading (HFT) exposed order books to rapid scrutiny, prompting institutional investors to seek private venues to execute large trades without tipping off the market.
Unlike public exchanges like the NYSE or Nasdaq, where buy and sell orders are visible, dark pools are private trading systems that conceal order details—price, quantity, and identity—until execution.
This protects institutions from price slippage and market manipulation. By 2025, dark pools account for 51.8% of U.S. stock trading volume, per recent data, evolving from a niche tool to a mainstream mechanism.
Dark pools differ from over-the-counter (OTC) crypto trading. Operators often use short selling to amass stock, delivering volume to buyers while reporting trades to regulators like FINRA via the DIX index. This reveals the transaction scale but obscures the initiating party’s identity, balancing privacy with oversight.
The Controversy of Centralized Dark Pools
Traditional pools, run by centralized operators, have faced scrutiny. In 2016, Barclays and Credit Suisse paid over $150 million in fines for violating SEC rules, accused of misrepresenting pool participants and favoring HFT firms.
In 2018, Citigroup settled for $12 million after leaking client order data, enabling HFT firms to profit $9 billion at clients’ expense.
These cases highlight a major flaw: centralized control breeds trust issues and conflicts of interest—problems Web3 aims to solve.
Web3 Dark Pools: A Decentralized Revolution
Reinventing Privacy with Blockchain
In Web3, dark pools leverage blockchain’s transparency while countering its downsides with cutting-edge cryptography.
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) and secure multi-party computation (MPC) enable private, verifiable trades without intermediaries. Smart contracts automate execution, ensuring traders retain custody of assets and eliminating the risk of operator abuse seen in Web2.
Web3 darkpools also offer programmable privacy. Developers can fine-tune what remains hidden—order details, for instance—while selectively disclosing results to regulators or auditors. This flexibility, impossible in traditional systems, positions Web3 as a game-changer for secure, private trading.
Why a Dark Pool Perpetual Contract DEX?
CZ’s proposal targets a critical flaw in DEXs: total transparency.
Public order books and on-chain data expose trades to miner-extractable value (MEV) attacks—frontrunning, backrunning, and sandwich attacks—where bots exploit visible orders, inflating slippage for large trades.
CZ noted, “If you want to execute an order of $1 billion, you must want to complete the transaction before the market notices it.” A darkpool DEX could shield such moves.
Perpetual contracts, a high-leverage staple of crypto trading, amplify this need. On-chain visibility of positions and liquidation prices invites manipulation. For example, malicious actors can target a whale’s liquidation price, crashing the market to trigger forced sales.
Recent cases, like Hyperliquid’s HLP liquidation and James Wynn’s $1.25 billion Bitcoin long position—sniped for a $17 million profit in a week—shpw the stakes.
Simon Kim, founder of Hashed, argues Web3’s transparency, while a strength, creates a “surveillance system” where AI and analytics track every move.
Even MicroStrategy’s Bitcoin holdings, 87.5% traced by Arkham Intelligence despite warnings from Michael Saylor, prove privacy’s fragility. Dark pools offer a shield, especially for institutional players entering Web3.
The Growth Imperative
Dark pools command over 50% of traditional finance volume, and CZ sees similar potential in crypto. Blocknative data shows private Ethereum transactions soaring from 4.5% in 2022 to over 50% of gas fees in 2025.
On Solana, wallets and bots now prioritize MEV protection, signaling a market hungry for privacy. As institutions flood crypto with big bets, dark pools could scale liquidity tenfold, per CZ’s vision.
How Web3 Dark Pools Work
Web3 projects are pioneering diverse approaches to on-chain privacy. Here’s a look at the tech and trailblazers:
1. Renegade
- Network: Arbitrum
- Tech: Combines MPC and ZKPs
- Approach: Traders manage balances and orders locally, submitting commitments, nullifiers, and validity proofs to smart contracts, akin to Zcash. Orders stay hidden pre-trade; only counterparties see post-trade asset swaps. Relayers run MPC via P2P networks, proving “VALID MATCH MPC” for secure, anonymous matching.
- Edge: No slippage, pegged to Binance’s mid-price for a Web2-like experience.
- Status: Live on Arbitrum, gaining traction for fully private DeFi.
2. Arcium
- Network: Solana
- Tech: MPC with additive secret sharing
- Approach: Encrypts shared states for on-chain computation without exposing data. Supports local additions and single-round multiplications. Developers define private states and functions via Solana programs, managed by the MXE virtual environment for parallel processing.
- Milestone: A dark pool demo on Solana’s testnet marks the chain’s first confidential venue, open to DeFi builders.
- Status: Scaling privacy for Solana’s high-throughput ecosystem.
3. Aztec
- Network: Ethereum
- Tech: ZK-Rollup
- Approach: Private functions run locally, generating proofs, while public ones execute on-chain. States use UTXO-style encryption, viewable only by owners. Paired with Ren Protocol, Aztec’s dark pool hides orders via Aztec Notes, updating encrypted states post-trade.
- Funding: $100 million Series B from a16z crypto in 2022.
- Status: A leader in Ethereum privacy solutions
Opportunities and Challenges
The Promise
Web3 dark pools could mirror traditional finance, capturing half of crypto trading volume as institutions demand privacy. They complement DEXs: small trades thrive on transparent price discovery, while big trades hide in dark pools. Beyond trading, privacy tech could transform AI, DePIN, and supply chains, making dark pools a cornerstone of Web3’s privacy revolution.
The Challenges
- Scalability: MPC and ZKP are resource-heavy, slowing large-scale trades. Renegade’s P2P complexity spikes with users, per Aztec’s Zac Williamson, who notes encryption bloats data, curbing throughput.
- Stability: Arcium’s Solana testnet demo crashed under high traffic, exposing the need for robust infrastructure and testing.
- Solution: Faster cryptographic libraries and optimized networks are critical to unlock mass adoption.
The Future of Dark Pools in Web3
CZ’s call for a dark pool perpetual contract DEX isn’t just a tweet—it’s a roadmap. By shielding trades from MEV, protecting whale positions, and scaling liquidity, dark pools could redefine DeFi. Projects like Renegade, Arcium, and Aztec are paving the way, blending privacy with blockchain’s transparency. As Web3 matures, expect dark pools to bridge institutional and retail needs, driving a private, secure, and efficient trading frontier.
What do you think? Could dark pools be the key to unlocking Web3’s full potential? Share your thoughts with Lumyna!



