What is blockchain?
It is a revolutionary digital ledger that records transactions or data across a distributed network of computers. Unlike traditional databases controlled by a single entity, blockchain operates without a central authority, making it a cornerstone of decentralized technologies. It’s best known for powering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but its applications extend far beyond finance, offering a secure and transparent way to store and share information.
Who invented blockchain?
It was introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonymous creator of Bitcoin, in 2009. Nakamoto’s whitepaper described it as a system to prevent double-spending in a digital currency without relying on banks. While Nakamoto pioneered its practical use, the concept builds on earlier cryptographic and distributed computing ideas. Since then, developers worldwide have expanded its capabilities.
When is is it used?
Blockchain operates 24/7, continuously recording and updating data as long as its network is active. It underpins cryptocurrencies every second of the day, ensuring transactions are processed globally. Beyond crypto, it’s employed in real-time applications like tracking goods in supply chains, verifying digital identities, or even securing election results, with usage growing steadily since its inception.
Where does it exist?
It exists on a global network of computers known as nodes. These nodes, run by individuals, organizations, or miners, store identical copies of the ledger, ensuring no single point of failure. For example, Bitcoin’s blockchain is maintained by thousands of nodes across continents, making it accessible and resilient worldwide.
Why use blockchain?
It is is valued for its transparency, security, and immutability. Every transaction or entry is visible to participants, cryptographically protected, and nearly impossible to alter once recorded. This eliminates the need for trusted intermediaries, reducing costs and risks in systems like banking or record-keeping, while empowering users with control over their data.
How does blockchain work?
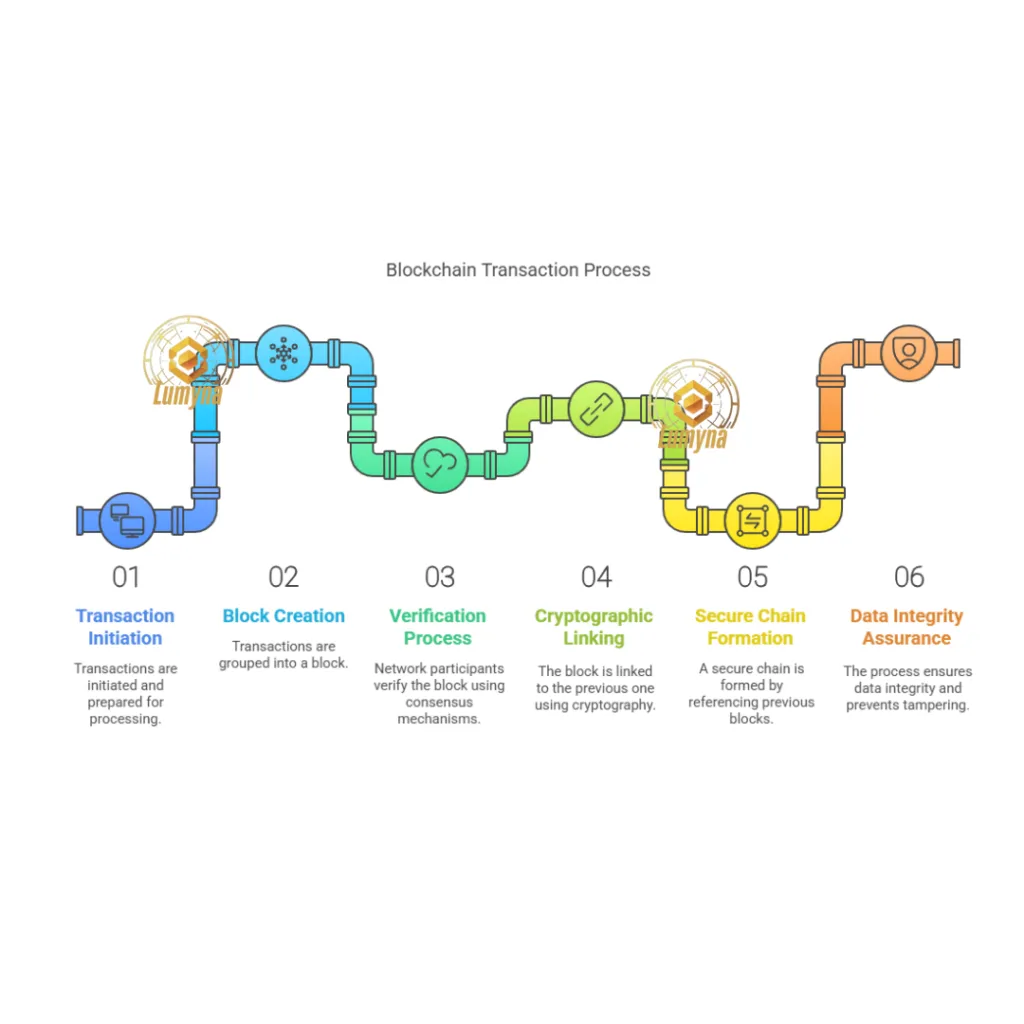
Transactions are grouped into blocks, verified by network participants (often through consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work), and linked chronologically using cryptography. Each block references the previous one, forming a secure chain. This process ensures data integrity and prevents tampering, as altering one block would require rewriting the entire chain across all nodes.
Related Questions:
- Is blockchain only for crypto? No, it’s also used in supply chain management, healthcare records, voting systems, and smart contracts, showcasing its versatility.
- Can blockchain be altered? It’s nearly impossible once data is confirmed, thanks to cryptographic hashing and network consensus.
- What’s a public blockchain? A public blockchain, like Bitcoin’s, is open to anyone, unlike private blockchains restricted to specific users or organizations.
- How secure is blockchain? Extremely secure, its encryption and decentralized structure make it highly resistant to hacking or unauthorized changes.