The “Genesis Block” is a foundational concept in blockchain technology, marking the origin of networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum. This glossary entry explores it using the 5 Ws and 1 H—Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How.
Who Created the Genesis Block in Blockchain?
The block is crafted by a blockchain’s founder or development team. For Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonymous creator, authored its block. Ethereum’s was built by Vitalik Buterin and his co-founders (e.g., Gavin Wood). These pioneers coded the initial rules and launched the chain. Miners or validators don’t create it—unlike subsequent blocks, it’s hardcoded. Nodes store it as the chain’s root, and users (e.g., via MetaMask) interact with networks built atop it.
What is a Genesis Block in Blockchain?
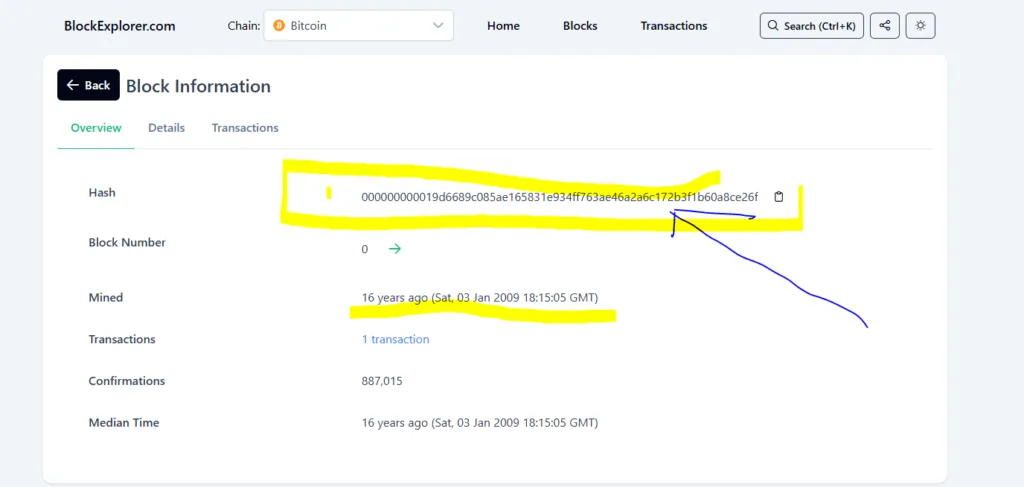
A “genesis block” is the first block in a blockchain, serving as the starting point of its ledger. Unlike later blocks, it has no previous block hash—its predecessor field is typically zeroed (e.g., 0000000000000000 in Bitcoin). It contains initial transactions or data, often symbolic, Bitcoin’s includes a 50 BTC reward (unspendable) and a hidden message. Ethereum’s genesis block set its initial state, like account balances for founders. Secured by cryptography (e.g., SHA-256), it’s the anchor for all subsequent blocks, defining the chain’s parameters.
When Was the Genesis Block Created in Blockchain?
The block’s creation marks a blockchain’s launch date. Bitcoin’s arrived on January 3, 2009, hardcoded by Satoshi. Ethereum’s debuted on July 30, 2015, after a crowd-sale. Other chains followed: Binance Smart Chain (April 2020), Solana (March 2020). It’s a one-time event—unlike regular blocks (e.g., Bitcoin’s 10-minute cycle), it’s not mined or validated dynamically. In 2025, these dates remain historical benchmarks, though forks (e.g., Ethereum Classic’s 2016 split) can spawn new genesis blocks.
Where is the Genesis Block Stored in Blockchain?
The block resides in the blockchain’s source code and is replicated across all full nodes. For Bitcoin, it’s embedded in Bitcoin Core software, stored on ~15,000 nodes globally (2025 estimate). Ethereum’s is in Geth or other clients, held by ~10,000 nodes. Physically, this spans hard drives worldwide—your laptop could host Bitcoin’s ~500 GB chain, starting with Block 0. Block explorers like Etherscan or Blockchain.com display it publicly. In Web3, tools like IPFS might archive related data, though the block itself stays on-chain.
Why is the Genesis Block Important in Blockchain?
The block is crucial for initialization and integrity. It defines a blockchain’s starting state, Bitcoin’s set a 21M coin cap, Ethereum’s enabled smart contracts. Without it, there’s no chain; it’s the root linking all blocks via hashes, ensuring immutability, altering it breaks everything. It often carries symbolic weight: Bitcoin’s message protested banks, cementing its ethos. In security, it’s a reference point, forks or attacks (e.g., 51% attacks) can’t undo it.
How is a Genesis Block Created in Blockchain?
Unlike mined blocks, a genesis block is manually coded into the protocol. Satoshi wrote Bitcoin’s in C++, embedding a timestamp and message: “The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout.” Ethereum’s team used JSON to specify initial allocations (e.g., 72M ETH pre-mined). No mining or staking occurs—it’s pre-generated, with a hardcoded hash (e.g., Bitcoin’s 000000000019d668…). Developers test it locally (e.g., via Foundry), then launch the network. Security-wise, its static nature avoids exploits like reentrancy, though misconfigs can doom a chain.
Expanded Insights for Web3 and Blockchain Enthusiasts
Let’s unpack this further. The genesis block is a blockchain’s birth certificate—unique, static, and symbolic. Bitcoin’s Block 0 isn’t just data; its message ties it to the 2008 financial crisis, a protest etched in code. Its 50 BTC reward? Unspendable, locked by design—Satoshi’s gift to history. Ethereum’s genesis allocated 72M ETH to crowd-sale backers, seeding its ecosystem. Solana’s, leaner, kickstarted its high-speed chain in 2020, per Solana Labs.
Technically, it’s an outlier. Regular blocks reference predecessors—genesis blocks don’t, making their hash (e.g., Bitcoin’s 000000000019d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f) the chain’s DNA. Ethereum’s JSON genesis file set gas limits and difficulty, a blueprint for smart contracts. In 2025, it’s still Block 0 on explorers—unchanged despite halvings or upgrades like EIP-1559. Forks create new ones—Ethereum Classic’s post-DAO hack (2016) reset its genesis, splitting the chain.
Security ties in. The block’s immutability anchors trust—double-spending can’t rewind to it. Tools like Phalcon (from your text) trace later blocks back to it, spotting anomalies.
Symbolism persists. Bitcoin’s message, decoded via Etherscan, resonates in 2025’s volatile markets. Ethereum’s genesis fueled a $500B ecosystem (2025 TVL estimate). In Web3, it’s lore and tech combined—IPFS might store its story, but the block lives on-chain.
Related Questions
- What is a genesis block in blockchain? – The first block, hardcoded at launch.
- Who created Bitcoin’s block? – Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009.
- When was Ethereum’s genesis block made? – July 30, 2015.
- Where is the block stored? – In source code and full nodes.
- Why does a genesis block matter? – It starts and defines the chain.
- How is a block different? – It’s not mined; it’s pre-set.
- What’s in Bitcoin’s genesis block? – 50 BTC and a bailout message.
- Who uses the genesis block today? – Nodes syncing the chain.
- When did Solana’s genesis block launch? – March 2020.
- Why can’t the block be changed? – It’s the chain’s immutable root.
- How was Ethereum’s genesis block coded? – Via JSON by its founders.
- What happens without a genesis block? – No blockchain exists.
- Who benefits from the block? – Founders, nodes, and users.
- How does it impact blockchain security? – It anchors the hash chain.




